Authentication
On the API auth is handled by Devise gem which provides Token based authentication.
This is wrapped in a GraphQL layer via GraphqlDevise allowing the front end to make authentication requests. A list of the available mutations and queries it supports can be found in the documentation here.
On login via GraphQL the API provides an opaque access token, as well as a client ID and UID.
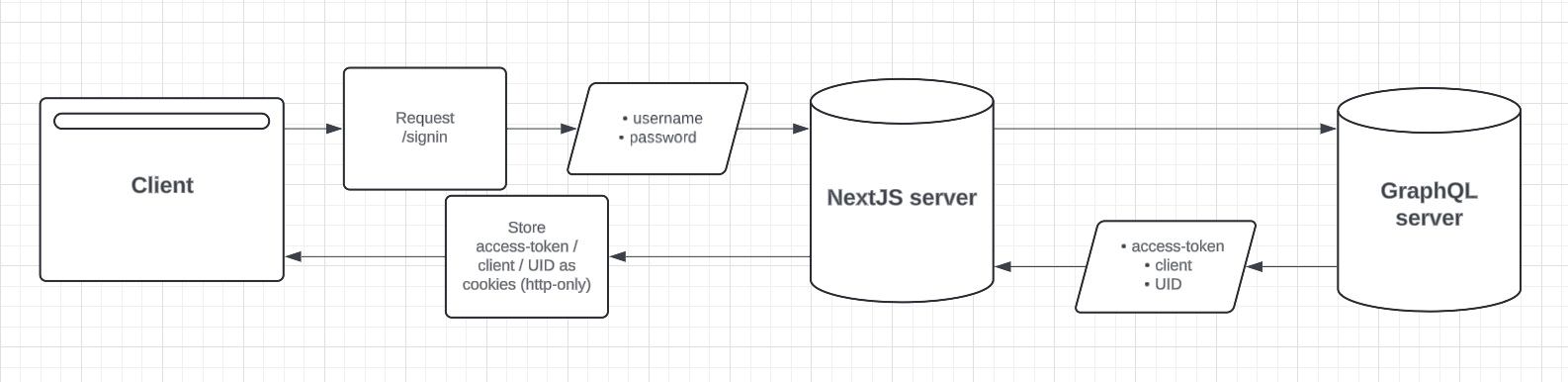
These are stored as cookies on the client with the HttpOnly attribute set so they cannot be accessed via javascript. These cookies are passed in the header of subsequent GraphQL queries to access information which should be restricted on a user by user basis.
On the server the users authenticated status is determined by checking for the existence of these cookies via the /authenticated route - if they exist the user can access pages that make calls to the API that require authentication.
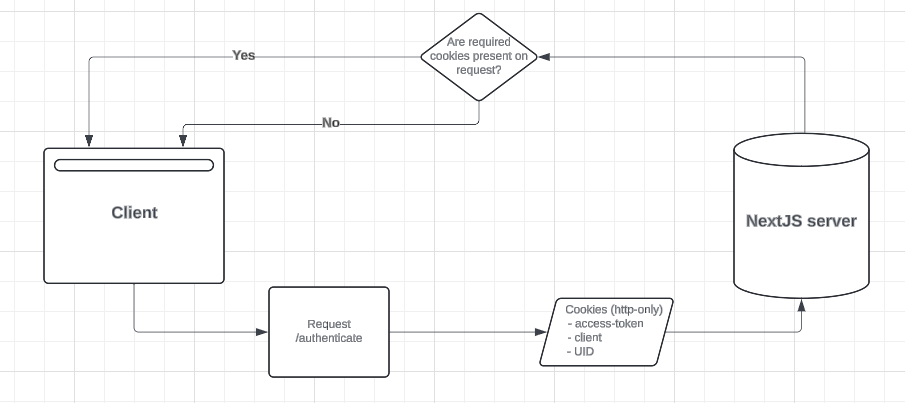
On the client side the useAuth hook provides the authenticated value. This is determined by executing a simple user query - if the user has the required credentials locally then the query will succeed and we know they are currently authenticated.
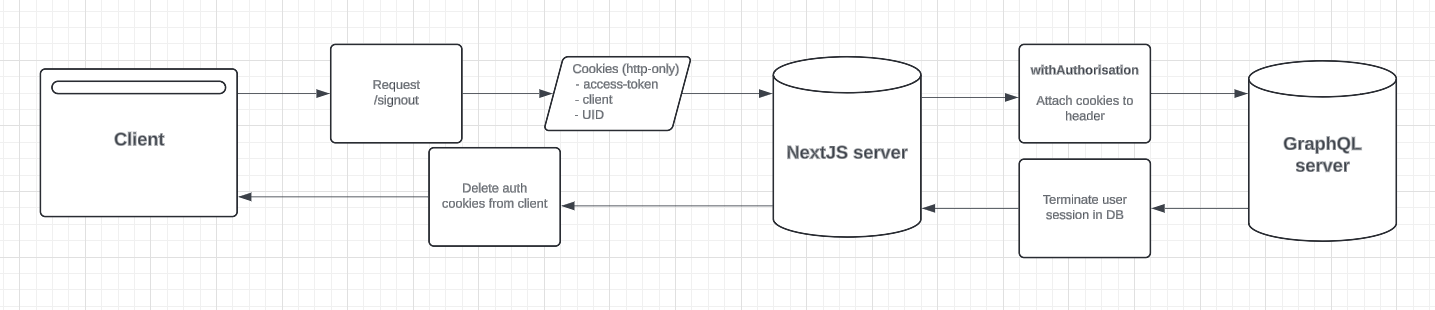
Signing out is a 2 step process - a request to the API terminates the clients session in the DB, after this successfully occurs the users cookies related to authentication are deleted from the browser.
useAuth hook
To simplify the development experience all the above methods are contained within the useAuth hook.
Authorising GraphQL requests
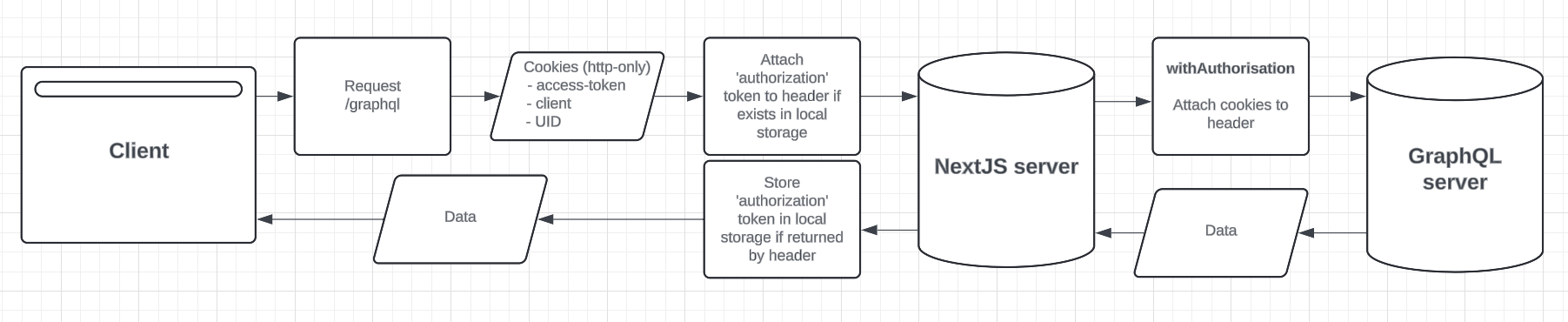
GraphQL requests are proxied through a NextJS API route. Here the required authorisation headers (access_token / client / uid) are attached to the request before it is forwarded on to the API endpoint. This process occurs in the withAuthorisation middleware. The authorize token also needs to be attached the to the header as well if it has been returned by the API previously, this is stored in local storage.
Protecting routes
Protected routes are routes which can only be accessed by logged in users. Using the withAuthorisation middleware we test each route to determine if the current user should be able to access it based on the presence of the cookies which are required to authenticate a request.